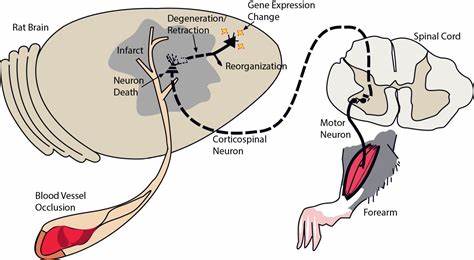
Alzheimer
Neuroscience
Purves D, Augustine GJ, Fitzpatrick D, Hall WC, Lamantia AS, McNamara JO, White LE. Neuroscience. 4th ed. Sunderland, MA. Sinauer Associates; 2008.
2016 Oct-Dec
1. Immunohistochemical localization of the calcitonin gene-related peptide binding site in the primate trigeminovascular system using functional antagonist antibodies. Neuroscience. 2016 Jul 22;328:165-83.
3. Evidence for the heterotetrameric structure of the adenosine A2A receptor-dopamine D2 receptor complex. Biochem Soc Trans.2016 Apr;44:595-600.
5. Hemorrhagic stroke incidence is declining faster than ischemic stroke in Joinville, Brazil: A population-based study over 18 years and systematic review. Neuroepidemiology 2016; 46:273.
7. Is Period3 genotype associated with sleep and recovery in patients with disorder of consciousness? Neurorehabil Neural Repair.2016 Jun;30(5):461-469.
9. Investigation of negative BOLD responses in human brain through NIRS technique. A visual stimulation study. Neuroimage. 2015 Mar;108:410-22.
11. Lipid Raft Alterations in Aged-Associated Neuropathologies. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(9):973-84.
14. Transient Micro-needle Insertion into Hippocampus Triggers Neurogenesis and Decreases Amyloid Burden in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Transplantation. 2016 25(10):1853-1861.
16. Prenatal Cocaine Exposure Upregulates BDNF-TrkB Signaling. PLoS One. 2016 Aug 5;11(8):e0160585.

2. Nerve growth factor enhances the CRE-dependent transcriptional activity activated by nobiletin in PC12 cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016 Jul;94(7):728-33.
4. Subcortical brain alterations in major depressive disorder: findings from the ENIGMA Major Depressive Disorder working group. Mol Psychiatry. 2016 Jun;21(6):806-12.
6. The spacing principle for unlearning abnormal neuronal synchrony. PLoS ONE. 2015; 10(2): e0117205.
8. Daphnane Diterpenes from Daphne genkwa Activate Nurr1 and Have a Neuroprotective Effect in an Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J Nat Prod.2016 Jun;79(6):1604-1609.
10. Differential expression of axon-sorting molecules in mouse olfactory sensory neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 2016 Aug;44(3):1998-2003.
12. AVN-101: A Multi-Target Drug Candidate for the Treatment of CNS Disorders. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 2016, 53(2): 583-620.
ization Properties of Histidine Residues in the Lipid Bilayer Membrane Environment. J Biol Chem.2016 Sep;291(36):19146-19156
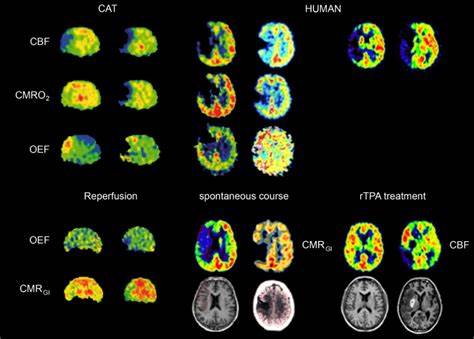
2016 Sept
1. Normative data for subcortical regional volumes over the lifetime of the adult human brain. Neuroimage. 2016 Aug 15;137:9-20.
3. Does vigabatrin treatment for infantile spasms cause visual field defects? An international multicentre study. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2015 Jan;57(1):60-7.
5. Evidence of motor-control difficulties in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, explored through a hierarchical motor-systems perspective. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2016;38(2):183-96.
7. Influence of workspace constraints on directional preferences of 3D arm movements. Exp Brain Res. 2015 Jul;233(7):2141-53.
9. Complementary assessments of executive function in preterm and full-term preschoolers. Child Neuropsychol. 2015;21(3):331-53.
11. Two Chronic Stress Models Based on Movement Restriction in Rats Respond Selectively to Antidepressant Drugs: Aldolase C As a Potential Biomarker. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Mar 26;18(10):pyv038.
14. The role of the acidic domain of α-synuclein in amyloid fibril formation: a molecular dynamics study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2016;34(2):376-83.
16. Dexmedetomidine attenuates neurotoxicity induced by prenatal propofol exposure. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2016 Jan; 28(1):51-64.
18. Neural responses towards a speaker’s feeling of (un)knowing. Neuropsychologia. 2016 Jan 29;81:79-93.
20. Development and preliminary validation of an Observation List for detecting mental disorders and social Problems in the elderly in primary and home care (OLP). Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2016 Jul;31(7):755-64.
22. The study of in vivo quantification of aluminum (Al) in human bone with a compact DD generator-based neutron activation analysis (NAA) system. Physiol Meas. 2016 May;37(5):649-60.
24. The role of cognitive reserve on terminal decline: a cross-cohort analysis from two European studies: OCTO-Twin, Sweden, and Newcastle 85+, UK. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2016 Jun;31(6):601-10.
25. Immunohistochemical localization of the calcitonin gene-related peptide binding site in the primate trigeminovascular system using functional antagonist antibodies. Neuroscience. 2016 Jul 22;328:165-83.
27. Dramatic Response After Lamotrigine in a Patient With Epileptic Encephalopathy and a De NovoCACNA1A Variant. Pediatr Neurol. 2016 Jul;60:79-82.
2. Changes in the BDNF-immunopositive cell population of neocortical layers I and II/III after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2015 Apr 24;1605:76-82.
4. Altered top-down cognitive control and auditory processing in tinnitus: evidences from auditory and visual spatial stroop. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2015 Jan; 33(1):67-80.
6. Sub-hubs of baseline functional brain networks are related to early improvement following two-week pharmacological therapy for major depressive disorder. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015 Aug;36(8):2915-27.
8. Geographic Variation of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Incidence in New Jersey, 2009-2011. Am J Epidemiol. 2015 Sep 15;182(6):512-9.
10. NEFL N98S mutation: another cause of dominant intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease with heterogeneous early-onset phenotype. Journal of Neurology 2016 Feb; 263(2): 361-9
12. Interferon-Stimulated Gene 15 Upregulation Precedes the Development of Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption and Cerebral Edema after Traumatic Brain Injury in Young Mice. J Neurotrauma. 2015 Jul 15;32(14):1101-8.
15. Attention that covers letters is necessary for the left-lateralization of an early print-tuned ERP in Japanese hiragana. Neuropsychologia. 2015 Mar;69:22-30.
17. Brain activities of visual thinkers and verbal thinkers: A MEG study. Neurosci Lett. 2015 May 6;594:155-160.
19. mRNA Levels of ACh-Related Enzymes in the Hippocampus of THY-Tau22 Mouse: A Model of Human Tauopathy with No Signs of Motor Disturbance. J Mol Neurosci. 2016 Apr;58(4):411-5.
21. Dynamical Behavior of Human α-Synuclein Studied by Quasielastic Neutron Scattering. PLoS One. 2016 Apr 20; 11(4): e0151447.
23. Early-onset motor impairment and increased accumulation of phosphorylated α-synuclein in the motor cortex of normal aging mice are ameliorated by coenzyme Q. Exp Gerontol. 2016 Aug;81:65-75.
26. Mutated Huntingtin Causes Testicular Pathology in Transgenic Minipig Boars. Neurodegener Dis. 2016;16(3-4):245-59.
2016 Aug
1. Improvement of cold injury-induced mouse brain edema by endothelin ETB antagonists is accompanied by decreases in matrixmetalloproteinase 9 and vascular endothelial growth factor-A. Eur J Neurosci. 2015 Sep;42(6):2356-70.
3. Isoallopregnanolone antagonize allopregnanolone-induced effects on saccadic eye velocity and self-reported sedation in humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2015 Feb;52:22-31.
5. Dysfunction in ribosomal gene expression in the hypothalamus and hippocampus following chronic social defeat stress in male mice as revealed by RNA-Seq. Neural Plast. 2016;2016:3289187.
7. Disinhibition reduces extracellular glutamine and elevates extracellular glutamate in rat hippocampus in vivo. Epilepsy Res. 2015 Aug;114:32-46.
9. Time course of spinal doublecortin expression in developing rat and porcine spinal cord: implication in in vivo neural precursor grafting studies. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Jan;35(1):57-70.
11. Near-transfer effects following working memory intervention (Cogmed) in children with symptomatic epilepsy: An open randomized clinical trial. Epilepsia. 2015 Nov;56(11):1784-92.
14. Can impaired working memory functioning be improved by training? – A meta-analysis with a special focus on brain injured patients. Neuropsychology (2016) Feb;30(2):190-212.
16. Prevalence and etiology of epilepsy in a Norwegian county – a population based study. Epilepsia. 2015 May;56(5):699-706.
17. Trace amine-associated receptor 1 regulation of methamphetamine intake and related traits. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Aug;40(9):2175–84.
19. The long-term impact of early life poverty on orbitofrontal cortex volume in adulthood: results from a prospective study over 25 years. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Mar;40(4):996-1004.
21. Is a neuronal chain between the pineal body and the retina in rats and hamsters? Transneural tracing studies. Neurosci Lett. 2015 Feb 19;588:1-6.
23. Direct Detection of α-Synuclein Dimerization Dynamics: Single-Molecule Fluorescence Analysis. Biophys J. 2015 Apr 21;108(8):2038-47.
25. Transplantation of neural progenitor cells in chronic spinal cord injury. Neuroscience. 2016 Apr 21;320:69-82.
27. Childhood-onset epilepsy five decades later. A prospective population-based cohort study. Epilepsia. 2015 Nov;56(11):1774-83.
2. Patterned, but not tonic, optogenetic stimulation in motor thalamus improves reaching in acute drug-induced Parkinsonian rats. J Neurosci. 2015 Jan 21;35(3):1211-6.
4. Aberrant Monoaminergic System in Thyroid Hormone Receptor-β Deficient Mice as a Model of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Jan 22;18(7):pyv004.
6. Characterisation of cell-substrate interactions between Schwann cells and three-dimensional fibrin hydrogels containing orientated nanofibre topographical cues. Eur J Neurosci. 2016 Feb;43(3):376-87.
8. Molecular architecture of the stria vascularis membrane transport system, which is essential for physiological functions of the mammalian cochlea. Eur J Neurosci. 2015 Aug;42(3):1984-2002.
10. Alcohol dependence and genetic variability in serotonin pathway among currently and formerly alcohol-dependent males. Neuropsychobiology. 2015;72(1):57-64.
12. Serotonergic mechanisms are involved in antidepressant-like effects of bisbenzylisoquinolines liensinine and its analogs isolated from the embryo of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertner seeds in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;67(12):1716-22.
15. Plasma oligomeric alpha-synuclein is associated with glucocerebrosidase activity in Gaucher disease. Mov Disord. 2015 Jun;30(7):989-91.
18. Nap it or leave it in the elderly: A nap after practice relaxes age-related limitations in procedural memory consolidation. Neurosci Lett. 2015 Oct 8;606:173-6.
20. Mechanisms and environmental factors that underlying the intensification of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, Ecstasy)-induced serotonin syndrome in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Apr;232(7):1245-60.
22. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype 7 in the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis is Essential for Intermale Aggression. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2016 Feb;41(3):726-35.
24. PIKfyve mediates the motility of late endosomes and lysosomes in neuronal dendrites. Neurosci Lett. 2015 Sep 25;605:18-23.
26. Dopamine Transporter Activity Is Modulated by α-Synuclein. J Biol Chem. 2015 Dec 4;290(49):29542-54.
ARCHIVE
2016 June
2016 Mar
2015 Nov
2015 May
2014 Dec
2013 Nov
2013 July
2013 May
BREAKING NEWS: Editors’ Picks
- A new study suggests Alzheimer’s disease may come from the brain infections. Science Translational Medicine, 2016 May.
The new study could change the way we think about the disease, and develop new drugs for treatment. - New Alzheimer’s disease causing proline substitutions. The EMBO Journal, Nov 3, 2015
The failure to develop efficient Alzheimer’s therapy might come from the pooling, in clinical experiments, of patients who suffer from distinct disorders that eventually lead to Alzheimer’s symptoms. Therefore it is essential to carefully characterize and classify the mechanisms that underlie Alzheimer’s disease, in order to allow for the development of novel therapies.
- Modulating brain’s stress circuitry might prevent alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, Nov 16, 2015.
long-term treatment using a small molecule drug that reduces activity of the brain’s stress circuitry significantly reduces Alzheimer’s disease (AD) neuropathology and prevents onset of cognitive impairment in a mouse model of the neurodegenerative condition.
- Alzheimer protein’s structure may explain its toxicity. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2015 May.
Knowing the physical structure of the 42 amino acid-long form of amyloid beta in the fibers is key to understanding how it folds up improperly and aggregates into toxic plaques.
- New link between diabetes and Alzheimer. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2015 May
A unique connection between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease has been uncovered, providing further evidence that a disease that robs people of their memories may be affected by elevated blood sugar.
- Major pathway (SARM1) identified in nerve cell death offers hope for therapies. Science, 2015 April
New research highlights how nerves start to die, a discovery that unveils novel targets for developing drugs to slow or halt peripheral neuropathies and devastating neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
- ‘Tangles’ trigger early-stage Alzheimer’s abnormalities in neocortical networks. Neuron, 2015 March.
The study’s dramatic results are due, in part, to the scientists’ decision to focus on a seldom-studied brain cell pathology known as “tangles”.
- Even mild traumatic brain injury may cause brain damage. Neurology, 2014 July.
Those with injuries had brain damage in brain white matter consisting of disruption to nerve axons. This finding is especially important, as 90 percent of all traumatic brain injuries are mild to moderate.
- Autophagy mediates the formation of amyloid beta plaques. Cell Reports, 2013 October.
The study sheds light on the metabolism of amyloid beta, and its role in neurodegeneration and memory loss. It might be a potential drug target for the treatment of the disease.
- XIAP Regulates Caspase Activity in Degenerating Axons. Cell Reports, 2013 August.
Excessive nerve cell pruning leads to disease. Scientists have made important discoveries about a cellular process that occurs during normal brain development and may play an important role in neurodegenerative diseases. The study’s findings point to new pathways and targets for novel therapies for Alzheimer’s.
- Prion-like proteins drive several diseases of aging. Nature, 2013 September
A new emerging concept that many of the brain diseases associated with aging, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, are caused by specific proteins that misfold and aggregate into harmful seeds. These seeds behave very much like the pathogenic agents known as prions, which cause mad cow disease.
 Euro
Euro
 US Dollar
US Dollar