Physician-diagnosed diabetes and the use of glucose-lowering medications for diabeteso
diabetes-obesity-2015-1-4
Physician-diagnosed diabetes and the use of glucose-lowering medications for diabetes
Hypertension was defined as ≥140/90 mmHg or use of hypertension treatment [13]. Type 2 diabetes was diagnosed according to a fasting glucose level in plasma ≥ 126 mg/dL (≥7.0 mmol/L) repeated on two consecutive days, or HbA1c above or equal to 6.5% (48 mmol/mol) or self-reported, physician-diagnosed diabetes and the use of glucose-lowering medications for diabetes

Impaired fasting glucose
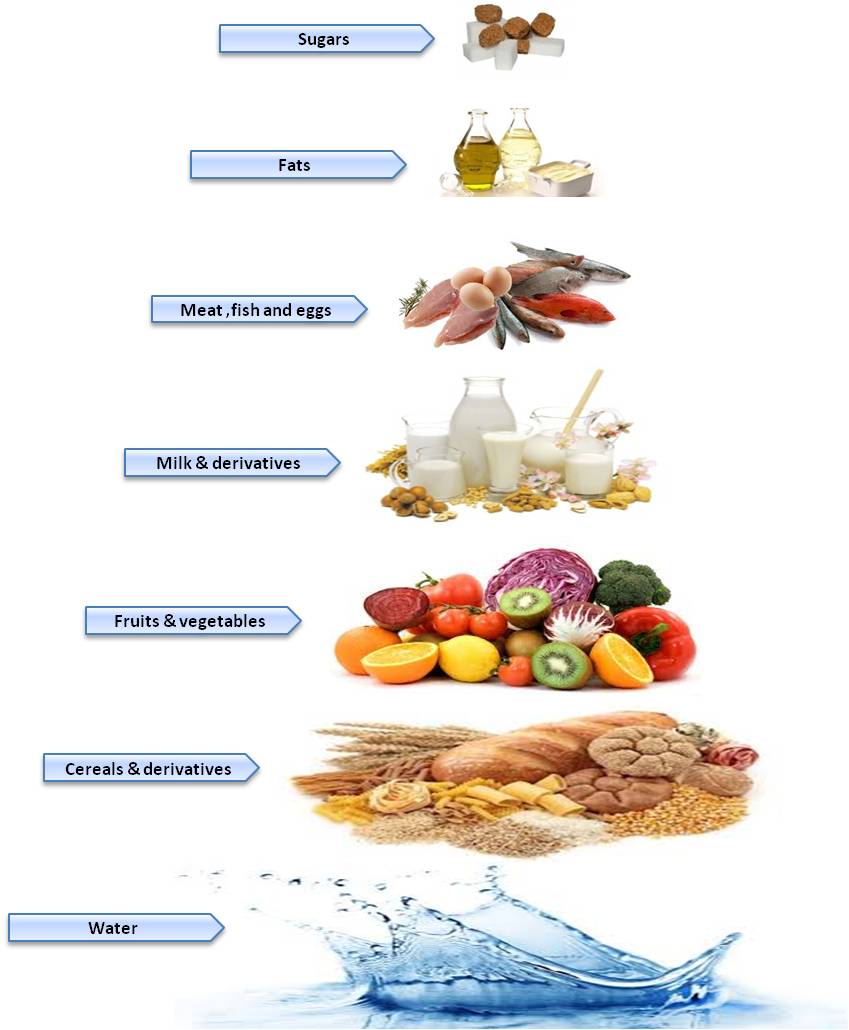
prediabetes was indicated by a fasting glucose level in plasma of 5.6–6.9 mmol/L (100–125 mg/dL) and a normal fasting glucose of <5.6 mmol/L (100 mg/dL) [19]. An insulin-resistant state was diagnosed in women with HOMA-IR >2.3 [20]. The median cutoff value for BCAAs was used [475.0 µmol/L (422.8–566.4); n = 349]. The 75th percentile cutoff values for total calcium (TCa), albumin-corrected calcium (CCa) and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were used [2.36 mmol/L (2.27–2.45); 2.26 mmol/L (2.20–2.38); 37.0 mmol/mol (33.0–39.0) n = 349, respectively]. The study participants continued their normal omnivorous diet regimen. None of them followed an elimination or high-protein diet. Dietary supplements, including BCAAs, calcium, vitamin D and protein supplements (e.g., whey, casein), were not used either. The women were divided into 2 groups.
- A normoglycemic group (NG, n = 184): women with a normal fasting glucose, without a history of diabetes, and with HOMA-IR < 2.3.
- A dysglycemic group (DG, n = 165): women with at least one of the following criteria: diabetes, prediabetes, HOMA-IR ≥ 2.3
diabetes-obesity World Biomedical Frontiers
 Euro
Euro
 US Dollar
US Dollar
